Nail fungus is called onychomycosis. Initially, the infectious process affects the thumb, but as it develops it spreads to other people. The disease goes through several stages. The sooner treatment is started, the easier it will be to deal with the problem. This is especially true in relation to the big toe of the lower limb - it has a large area and size, therefore the degree of injury is significant.
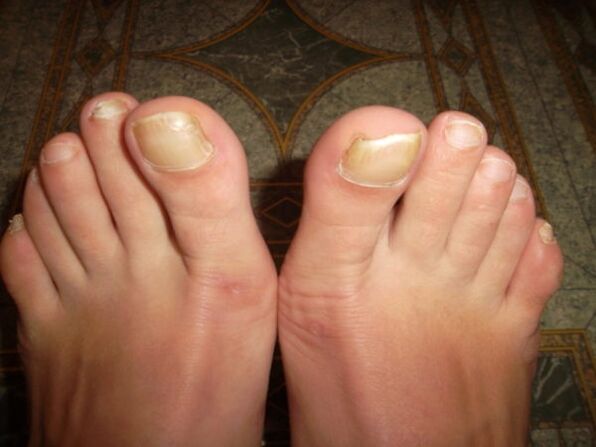
Stages of onychomycosis
Nail fungus goes through several stages of development, each of which is characterized by certain symptoms. The following stages of development of the disease are distinguished:
- Original.At this stage, no visible pathological deviations are observed: the changes are still external. The nail plates on the toes of the lower extremities lose their shine. White spots or stripes appear on the surface. In general, the nail looks healthy, the person does not feel pain or discomfort. If you identify nail fungus at this stage, you can get rid of it quickly.
- Moderate or progressive.The structure of the nail already undergoes pathological changes. The nail acquires a pronounced yellowish tint, peels off and crumbles. There is also an unpleasant odor coming from the affected foot.
- Advanced or dystrophic stage.Deep damage to the nails occurs. In this case, the infectious process passes from the thumb to the rest. The entire surface of the nail plate is affected by the fungus and it detaches from the bed and becomes loose. The patient is bothered by severe itching. When pressing on the affected areas, a painful, throbbing sensation occurs. For this reason, the patient should not wear closed shoes.
%20stage%20of%20onychomycosis.jpg)
At the third stage of development of the infectious process, infection of the skin of the foot is possible. In this case, the fungus can only be cured with the help of complex therapy, which involves the use of local and systemic medications (tablets for oral administration).
Reasons for the development of fungus on the big toe
The main reasons that cause the development of onychomycosis are:
- contact with a person with a fungal infection;
- neglect of hygiene rules;
- wearing someone else's shoes or narrow shoes that don't fit;
- weakened immune system;
- visit a bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool or beauty salon, where non-disinfected instruments can be used;
- trauma to the nail and surrounding skin;
- flat foot;
- prolonged use of antibacterial medications;
- hyperhidrosis (increased foot sweating);
- the presence of endocrine or immunological lesions;
- disorders in the circulatory system, which are especially important for elderly patients;
- phlebeurism;
- diabetes.
An important factor that increases the risk of developing onychomycosis is old age. Elderly people suffer from a lack of blood supply to their extremities, which also increases the risk of developing fungal infections.
The disease-causing agent reaches the nails or skin through infected objects or through contact with a carrier. The pathogen spreads quickly, invading new areas. The fungus enters the subungual space through damaged areas of the nail plate or surrounding skin.
The fungus quickly spreads to the nail bed. The rate of advancement exceeds the rate of plaque growth. Soon the pathogenic microorganism reaches its target and causes changes in the structure of the nail. It has been established that men suffer from fungus 3 times more often. Nail plates are affected by types of fungi such as dermatophytes, mold and yeast.
When should you see a doctor?
You should see a doctor at the first sign of a fungal infection. You should not wait for clear signs of the disease to appear - the formation of white spots and even a slight itch in the foot area should be a reason to consult a specialist - a mycologist or dermatologist.
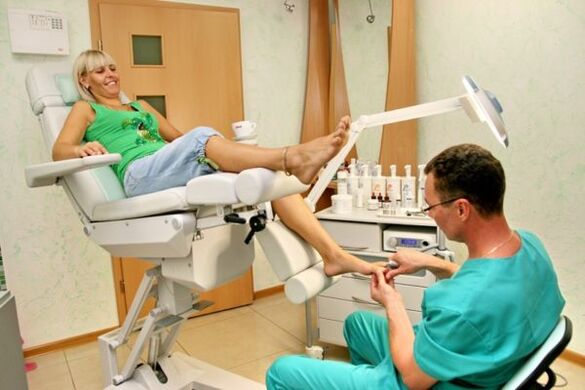
Diagnosis
Diagnostic measures to identify the disease and its stage include:
- visual inspection of the nail plates;
- take a tissue sample from the affected nail;
- cultural examination - inoculation of the material received by the patient into a nutrient medium to identify the type of microorganism that affected the nails.
In some cases, the specialist makes a differential diagnosis and separates onychomycosis from diseases such as lichen planus, psoriasis and keratoderma.
Treatment of fungal nail infection at an early stage of development
If the disease is detected early, it will be much easier to deal with it. In this case, it is generally sufficient to use local agents that directly affect the affected nail.
In the first stage of mycosis, if no more than 50% of the nail plate is affected, the following medications are prescribed:
- Varnish that must be applied to the surface of the affected nails. This must be done twice a day, the total course of treatment will be one month. The product has contraindications, therefore it can only be used as prescribed by a doctor.
- Product produced in cream form. The main active ingredient kills almost all types of fungi. The cream is applied 3 times a day, the treatment lasts about a month.
- Product that is plaster impregnated with a special composition. The adhesive strips are left for 3 days and then removed. Special substances that cover the surface of the plaster help soften the nail plate and can be easily removed with manicure instruments or scissors.
- Medicine that contains a substance that destroys the fungus and prevents its proliferation. It is recommended to rub the affected areas 1 to 2 times a day. The duration of treatment depends on the condition of the nail plate and can vary from two to four weeks.
Any medications intended to treat mild forms of nail fungus should be prescribed by a doctor.
Advanced therapy for onychomycosis
In severe cases of the fungus, as well as in the case of an ongoing infectious process, complex treatment is indicated. Systemic antifungals should be prescribed if there are no contraindications. The patient receives the following medications:
- Systemic antibiotic from the triazole group in tablet form. The active substance of the drug reaches the location of pathogenic microorganisms and has a fungicidal effect.
- Medicine from the imidazole group that inhibits the development of pathogenic microorganisms and destroys them. The course of treatment and dosage are determined by the attending physician. The product causes adverse reactions.
- Medicine from the allylamine group with fungicidal effect. The active substance gradually accumulates in the layers of the nail plate, which makes it possible to destroy even fungi that are located quite deep.
In addition, with advanced nail fungus, procedures are effective in eliminating the infected plate. This can be done in the following ways:
- Surgical excision.This method involves lifting the plate with a sharp surgical instrument and removing it from the bed. After the operation, a bandage is applied. The surgical method is traumatic and rarely used. Instead, minimally invasive methods are practiced.
- Removing plaque with chemicals, promoting rapid exfoliation of the affected nail. In this case, the problem area is treated with a special solution, the medication is awaited and then products are used that help to quickly separate the plate from the nail bed.
- Laser treatment.This is a modern and painless method that quickly eliminates nail fungus. The laser acts on the plate, bringing it to high temperatures as quickly as possible. The beam penetrates deeply and neutralizes pathogens. The method is bloodless and absolutely safe, as it does not cause burns.
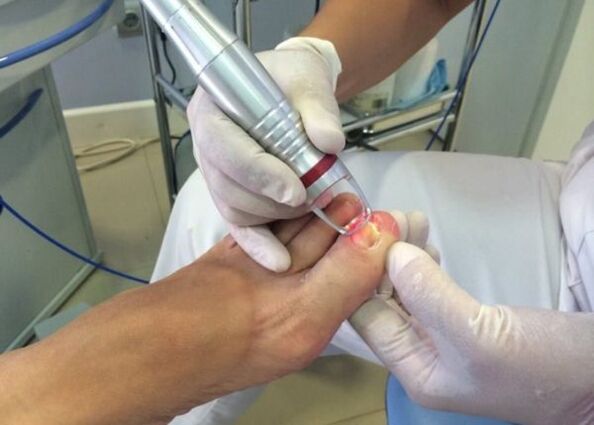
In the advanced stages of onychomycosis, it is necessary to strictly follow the doctor's recommendations, as the lack of adequate treatment increases the risk of widespread damage to the body by a fungal infection.
Traditional methods
Nail fungus can also be cured with traditional medicine. Such methods are of an additional nature and cannot be the basis of therapy. The most popular folk remedies include:
- Onion pulp.It is necessary to grate some onions and apply the resulting mass to the affected nails. Secure the top with a bandage. Leave it on for 15-20 minutes and rinse.
- Hydrogen peroxide.First, soak the affected feet in a water bath to soften the nails as much as possible. Then remove the top layer from the dish. Soak a piece of gauze in hydrogen peroxide and wrap the phalanx of the finger with the affected nail, capturing the immediate injury. Leave for 40-50 minutes. You can repeat the procedure up to twice a day.
- Apple vinegar.It is important to use a natural product. Take 2 tablespoons of vinegar and add the same amount of vodka and a tablespoon of glycerin. Dip a cotton swab in the resulting mixture and apply it to your nails for 15 minutes. Repeat 4 times a day.
Traditional recipes help to alleviate the severity of the symptoms of the disease and eliminate discomfort, but they are not able to destroy the causative agents of the disease.
The course of the disease and features of the treatment of nail fungus in children
Onychomycosis is rare in children. The main cause of the disease is weak immunity due to incomplete formation. Symptoms of onychomycosis in children are:
- the plaque loses its natural pink color, gray or white spots appear on the surface;
- irregularity and tuberosity of the nail plates;
- brittle and brittle nails;
- redness and swelling of the skin around the child's infected nail.
To treat nail fungus in children, only topical preparations such as spray, varnish or cream are generally used. If necessary, systemic agents are also prescribed. Antifungal medicines for oral administration should only be prescribed by a doctor.
Features of treatment in pregnant and lactating women
During pregnancy, there is a high risk of developing onychomycosis if the woman has already suffered from the disease and has not completely cured it. This is due to the weakening of the immune system that occurs during pregnancy.
It is important to treat the fungus in a timely manner, as in severe cases it creates a risk of bacterial infection that threatens the health of the mother and fetus. Systemic medications should not be used during pregnancy, as they have a high level of toxicity.
During pregnancy and lactation, topical medications should be used, but only those that are safe for the pregnant woman and her baby. These include salicylic ointment with sulfur.
Treatment of the elderly
In the elderly, decreased immunity is a natural, age-related phenomenon that creates additional risks for the development of onychomycosis. In this case, the specialist is also cautious when choosing a remedy to treat nail fungus.
Systemic medications are prescribed if the disease lasts a year or more, as well as for extensive lesions and degenerative changes in the nails.
Most often, elderly patients are prescribed systemic antifungal drugs from the allylamine and triazole group.
Preventive measures
If you have signs of fungus on your little finger or thumb, see your doctor immediately. But steps can be taken to prevent the development of this disease. The following recommendations must be observed:
- wash your feet at least once a day;
- wash socks every day and wear clean socks;
- if you sweat excessively, use special foot deodorants;
- Wear shoes of the right size, they should not be too tight and they should be washed daily;
- use only personal hygiene products, as well as manicure and pedicure tools;
- when visiting the pool, beach, sauna, wear personal rubber shoes;
- After visiting the pool, sauna, wash your feet with soap and water, if necessary, use pharmaceutical preparations for prevention.
Nail fungus is a disease that is quite difficult to cure at an advanced stage. At the first symptoms you should consult a doctor. Treatment depends on the stage of development of onychomycosis: in the initial phase, local medications are sufficient; when initiated, systemic antifungals are required.

















